IT Service Management
Section 1 : Overview
Apa itu service management ?
Service is an intangible product that brings utility or value to the customer. Service Management is thus a managerial discipline focused on a customer and a service. Service management is multidisciplinary field which is related to many other management fields.
Section 2 : The Service Lifecycle
SERVICE STRATEGY VALUE
This phase allows an organization to understand the following:
- Services that will be provided
- Customers of the service
- Value of the services
- Cost/risk associated with delivering the service
- Capacity of the organization to deliver the service
Service Design ensures that service organizations can deliver quality, cost-effective services and meet all of the business’ requirements for the planned services. It also provides the following benefits:
- Improved consistency of service
- Easier implementation of new or changed services
- Improved service alignment with business needs
- Improved IT governance
- Improved quality of service
Effective Service Transition adds value to the business by:
- Ensuring that all changes comply with business and governance requirements
- Using contingency plans to manage the level of risk during and after the service implementation (for example, service outage, service disruption)
- Improving the consistency and quality of the implementation process for new or changed services
Each phase in the ITIL Service Lifecycle builds value for the business and culminates in the business value delivered by Service Operations. For example:
- In Service Strategy, the service is modeled
- In Service Design and Service Transition, the service is designed and developed, and the cost is predicted and validated
- In Service Operations, services are delivered and measured against agreed customer committments.
- In Continual Service Improvement, the measures for optimization are identified
With Continual Service Improvement, organizations can identify and implement improvements to IT services and realize many benefits, including:
- Better information about current services (and possibly about areas where change would bring increased benefits)
- Improved service reliability, stability, and availability
- Improved resource allocation and utilization
- Improved metrics and management reporting
- Clearer view of current and future IT service capability
- Better working relationships between customers and IT organization
- Enhanced customer satisfaction
Business Relationship Management
Financial Management For IT Service
Demand Management
Service Portofolio Management
Design Coordination
Service Catalogue Management
Service Level Management
Supplier Management
Capacity Management
Availability Management
IT Service Continuity Management
Information Security Management And Access Management
Section 4 : Measurement, Metrics, And The Deming Cycle

Measurements and Metrics A measurement is an indication of the size, quantity, amount or dimension of a particular attribute of a product or process. For example the number of errors in a system is a measurement.
A Metric is a measurement of the degree that any attribute belongs to a system, product or process. For example the number of errors per person hours would be a metric.
Thus, software measurement gives rise to software metrics.
Metrics are related to the four functions of management:
- Planning
- Organising
- Controlling
- Improving

Metric Classification Software metrics can be divided into two categories; product metrics and process metrics.
Product metrics are used to asses the state of the product, tracking risks and discovering potential problem areas. The team's ability to control quality is assessed.
Process metrics focus on improving the long term process of the team or organisation.
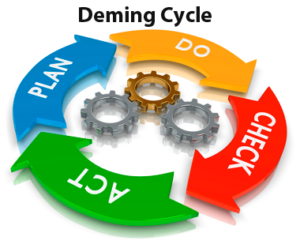
Plan: Establish the objectives and predict the result. Plan ahead to deliver results in accordance with the expected output (the target or goals).
Do: Implement the plan, execute the plan by taking small steps in controlled circumstances and make the product. Collect data for charting and analysis in the following check and act steps.
Check: Study the actual results (measured and collected in do phase above) and compare against the expected results (targets or goals from the plan phase) to ascertain any differences.
Act: Take action to standardize or improve the process

Komentar
Posting Komentar